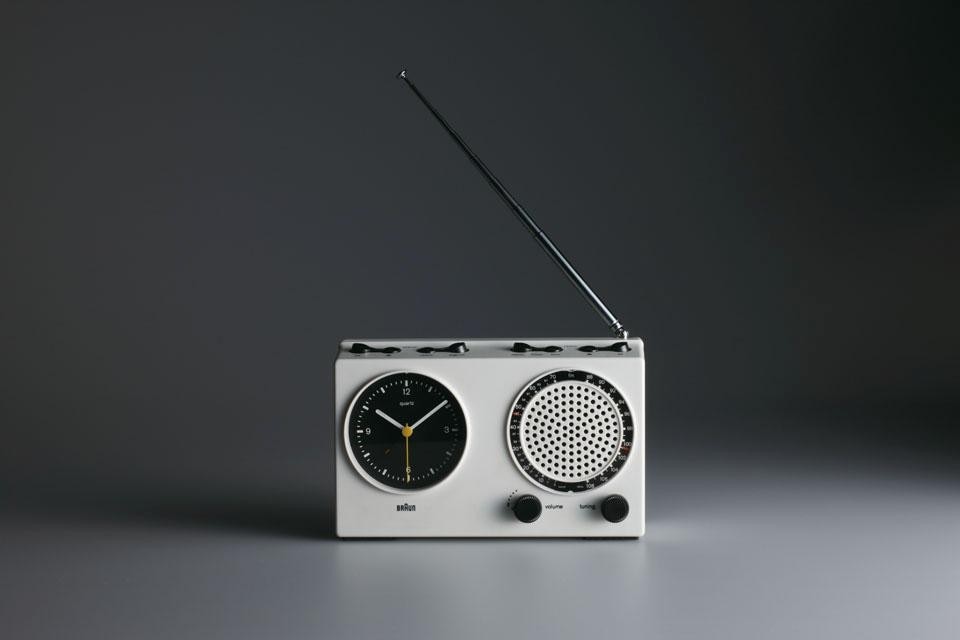
Dieter Rams is widely regarded as one of the most influential industrial designers of our time. Many of his works have achieved iconic status, while his ideas—in particular his advocacy for "less but better" design—have proved formative for a contemporary culture concerned with design ethics and sustainability. For more than 40 years, Rams was the lead designer for the German electrical appliance company, Braun, and the British furniture company Vitsœ. The exhibition, originally organized and produced by Suntory Museum Osaka in collaboration with Fuchu Art Museum in Japan, presents a survey of the designer's work and includes a section on the legacy of Rams in contemporary design.
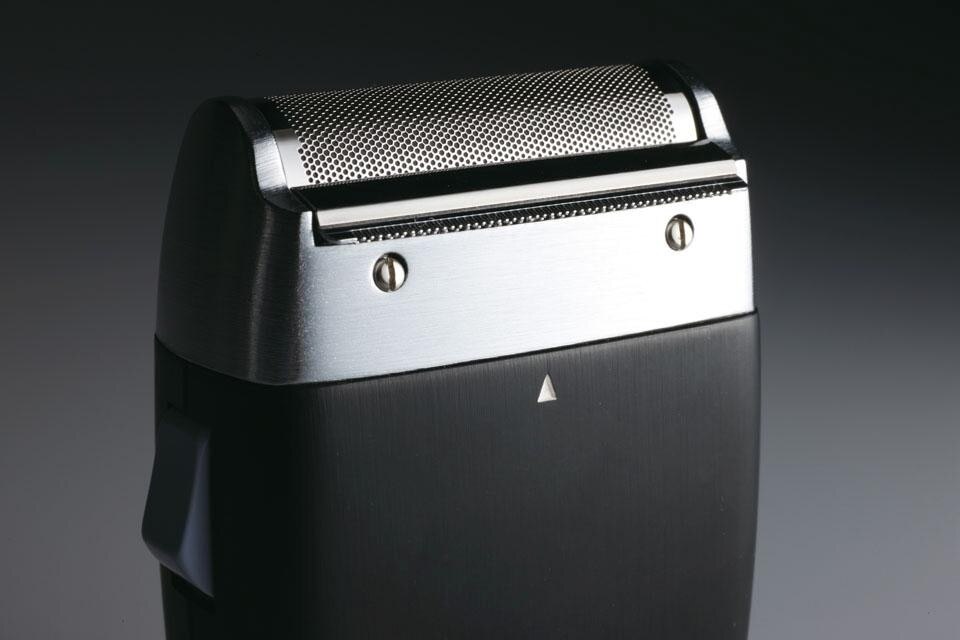
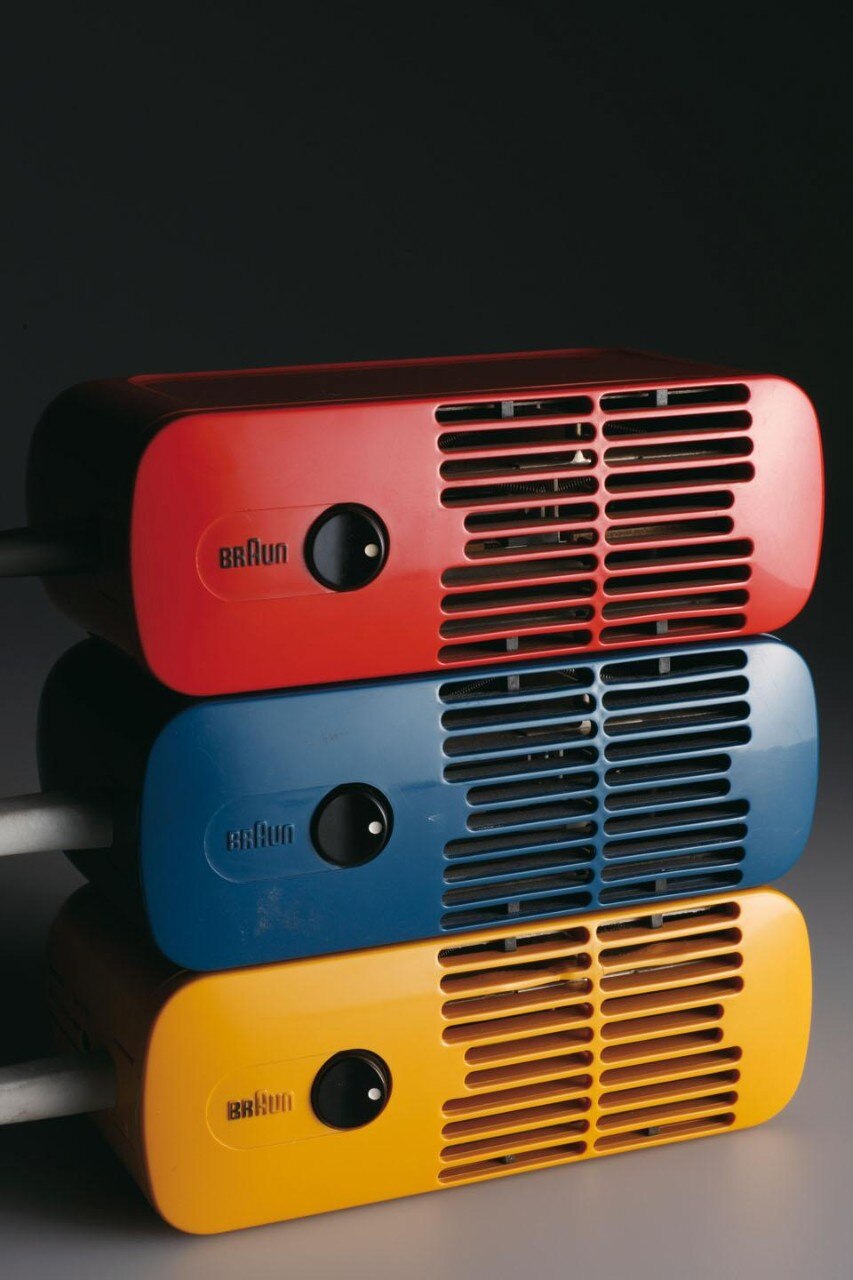
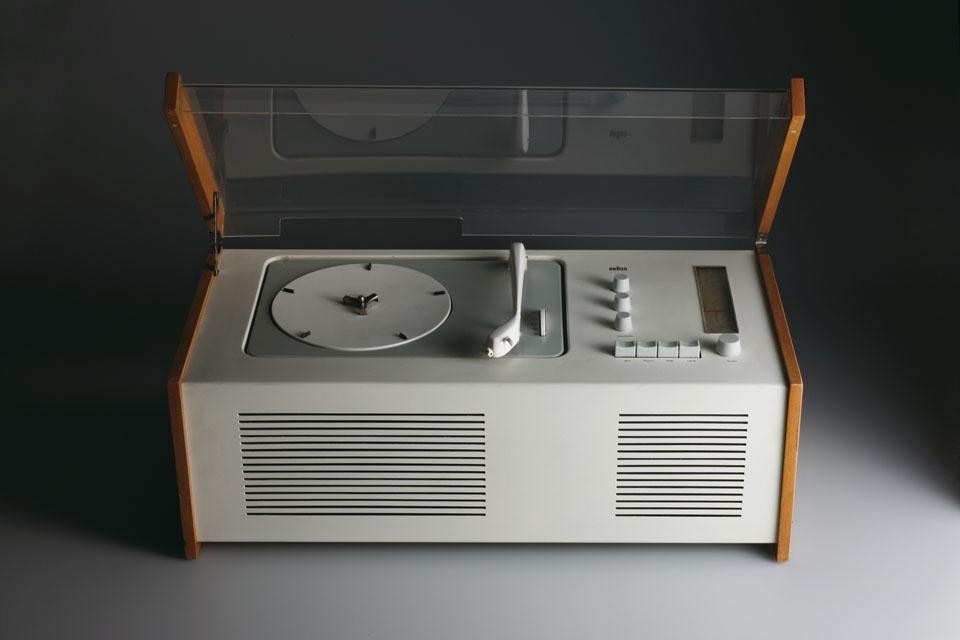
Ever concerned with craft and technique, Rams (b. 1932) studied architecture at the Werkkunstschule Wiesbaden. After working for architect Otto Apel in the 1950s, Rams joined the electronic devices manufacturer Braun in 1961 as chief of design, a position he kept until 1995. While at Braun, Rams ushered in a new wave of holistic attention to domestic products, forever changing the relationship between design and the consumer. With over 500 products designed by him and his team, Rams's contribution to the history of industrial design is immense. Simultaneous to Rams's work with Braun, he collaborated with German company Vitsœ & Zapf (later British Vitsœ), which started production of his furniture designs in 1959. In 1960 Rams designed the acclaimed 606 Universal Shelving System, which is still being produced by Vitsœ today.
Rams's personal vision and philosophy was so entwined with the Braun brand and image that it is no wonder that the two names are nearly synonymous. In a 1989 interview with Taz magazine about Braun, Rams responded as both designer and company: "We are economical with form and colour, prioritize simple forms, avoid unnecessary complexity, do without ornament. Instead [there is] order and clarification. We measure every detail against the question of whether it serves function and facilitates handling."
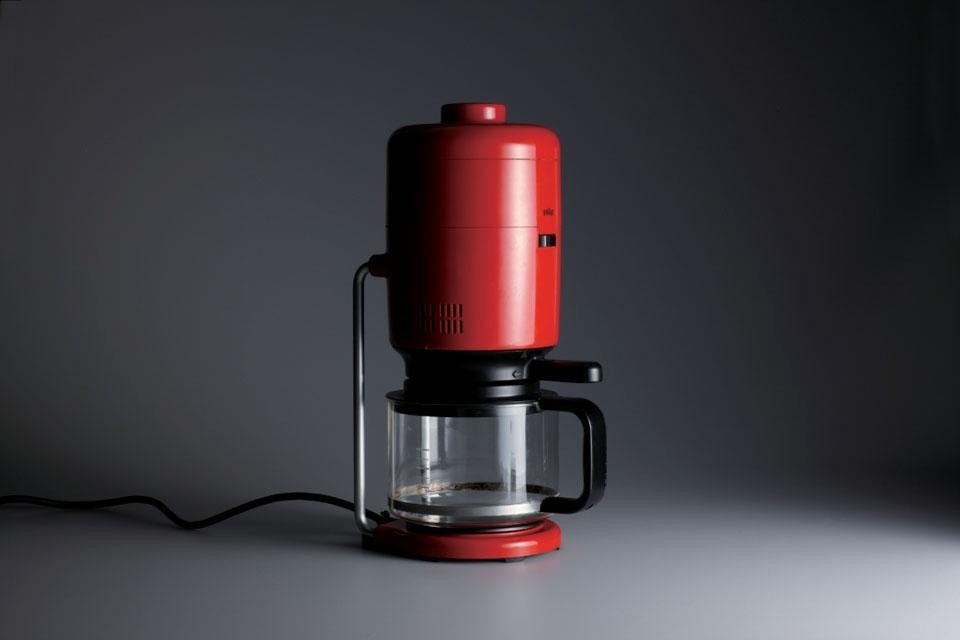

The exhibition will feature a vast array of the prolific designer's oeuvre, framing the works within the historical context as well as presenting a small selection of contemporary works inspired by Rams's coherent balance of aesthetics and functionality. Models and designs by Rams, never before shown to the public, will be presented as a means of reconstructing the development process and his specific design methodology. The Braun and Vitsœ corporate identity including some advertising and print media will also be presented.

Good Design Is Innovative— The possibilities for innovation are not, by any means, exhausted. Technological development is always offering new opportunities for innovative design. But innovative design always develops in tandem with innovative technology, and can never be an end in itself.
Good Design Makes a Product Useful—A product is bought to be used. It has to satisfy certain criteria, not only functional but also psychological and aesthetic. Good design emphasizes the usefulness of a product while disregarding anything that could possibly detract from it.
Good Design Is Aesthetic—The aesthetic quality of a product is integral to its usefulness because products are used every day and have an effect on people and their well-being. Only well-executed objects can be beautiful.
Good Design Makes A Product Understandable—It clarifies the product's structure. Better still, it can make the product clearly express its function by making use of the user's intuition. At best, it is self-explanatory.
Good Design Is Unobtrusive— Products fulfilling a purpose are like tools. They are neither decorative objects nor works of art. Their design should therefore be both neutral and restrained, to leave room for the user's self-expression.
We are economical with form and colour, prioritize simple forms, avoid unnecessary complexity, do without ornament.

Good Design Is Long-lasting— It avoids being fashionable and therefore never appears antiquated. Unlike fashionable design, it lasts many years – even in today's throwaway society.
Good Design Is Thorough Down to the Last Detail—Nothing must be arbitrary or left to chance. Care and accuracy in the design process show respect towards the consumer.
Good Design Is Environmentally Friendly—Design makes an important contribution to the preservation of the environment. It conserves resources and minimises physical and visual pollution throughout the lifecycle of the product.
Good Design Is as Little Design as Possible—Less, but better – because it concentrates on the essential aspects, and the products are not burdened with non-essentials. Back to purity, back to simplicity.

until February 20, 2012
San Francisco Museum of Modern Art
Organized by Joseph Becker, SFMOMA assistant curator of architecture and design