“Do you think it is possible for you to build us a ‘good’ school?”
What is a “good” village school? The poor conditions of China’s Loess Plateau region (north-west China) demand serious re-thinking. The fragile ecological conditions, coupled with having some extreme climatic conditions poses severe environmental and sustainable challenges to designers. The poor economy has restricted interventions and solutions. Villagers needing to leave their village homes to find work in the city further drain the social lineage; they leave their children behind but still hoping that they can be educated and one day make it in the society. They put their faith in their village schools.
Like many donated schools that have been built in the region, a way they iconize them is as follow: “The school is very modern with nice white tiles. We take pictures in front of them when they open. By the way, if they can also install air conditioners for us in the summer and heaters in the winter, it would be very good as otherwise it can be quite uncomfortable.”
We know for sure that something needs to be done. The project commenced in 2002. We wished to build a “demonstration” school that can showcase appropriateness and can address the environmental, social and economical dimensions of sustainability.
The Site
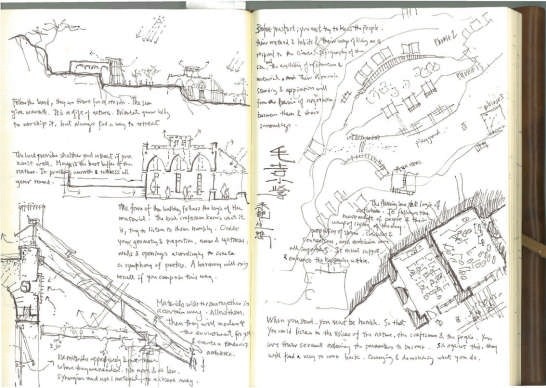
“The village head took the design team to a site that is south facing and surrounded by low hills. He told the team that it is the best site they have; and he hopes it is good enough for the school.”
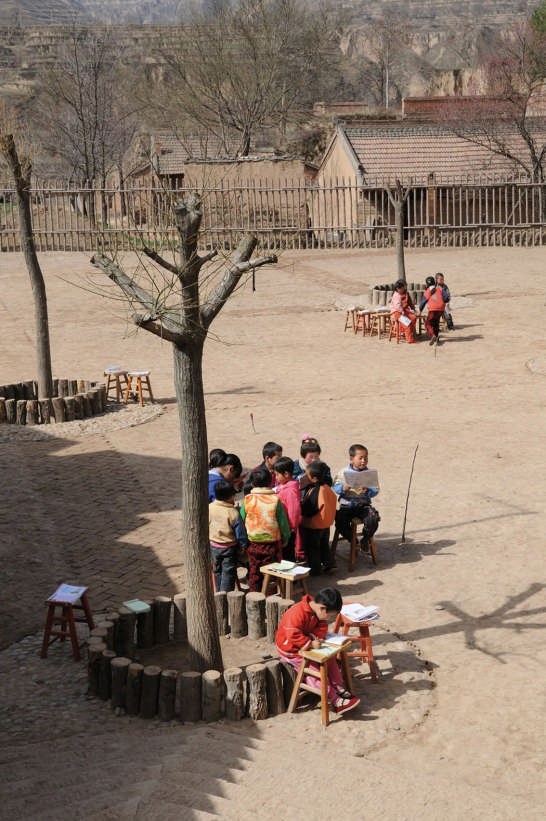
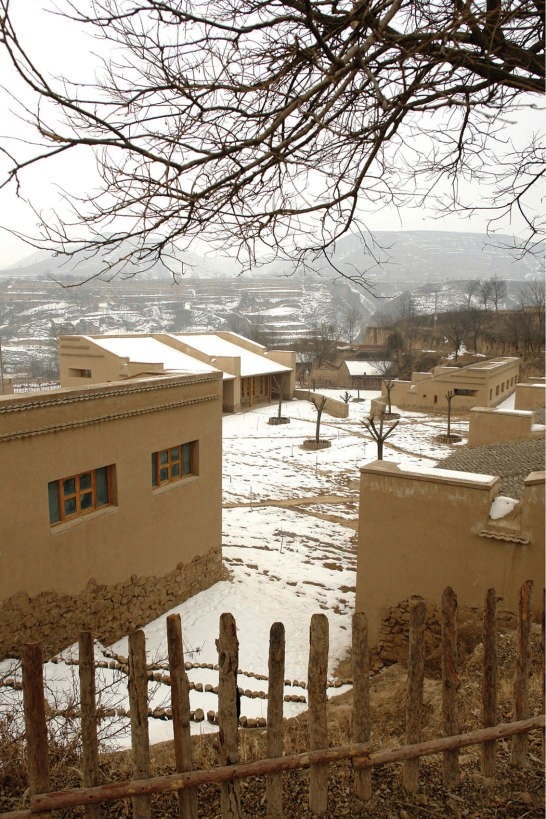
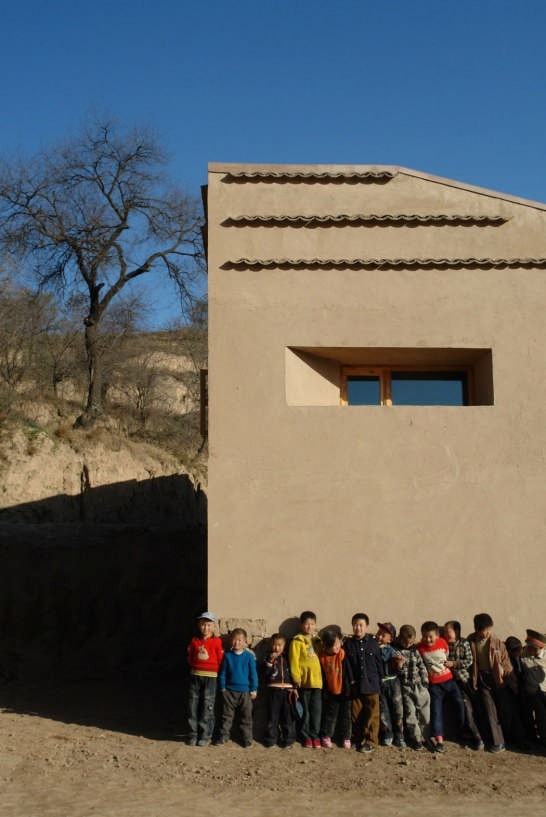
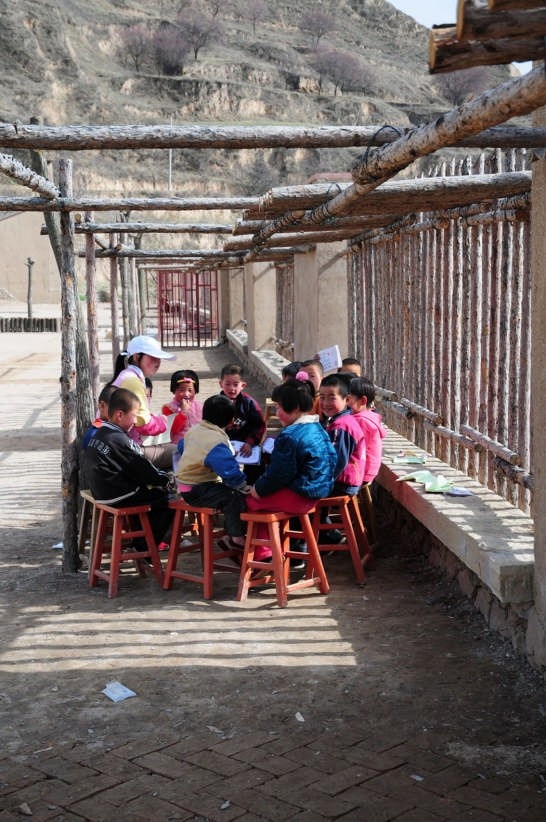
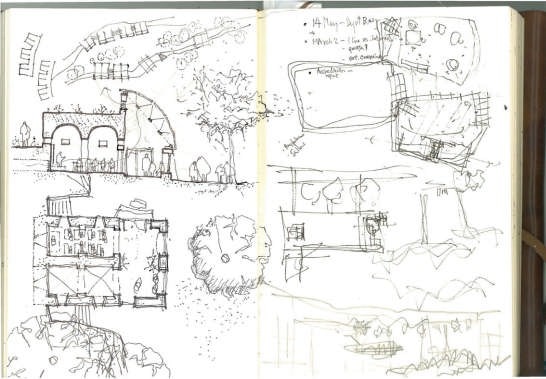
The project is located in the village of Maosi, in Gansu province, 6 hours drive from Xian. The tranquil and unspoiled setting reminds one that the village and its life have always been like that for hundreds if not thousands of years. It is only very recently that the onslaught of modernity and urbanisation is beginning to intrude. The village has around 2500 villagers and 200 students. Their existing schools are either in caves or in simple single storey brick huts.
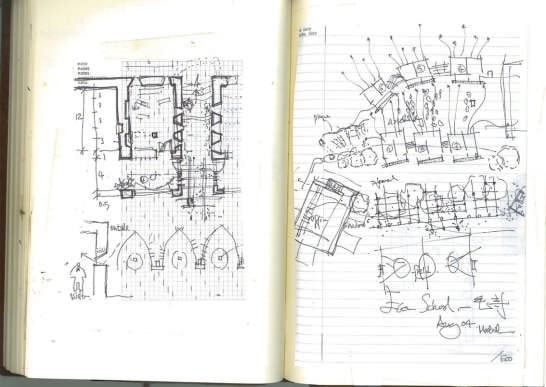
Methodology and Design
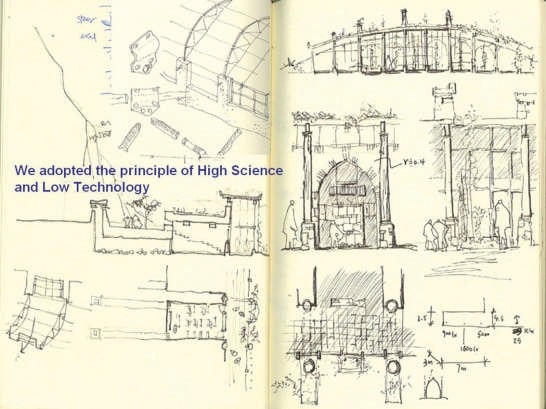
“High science and low technology is a motto of the working.”
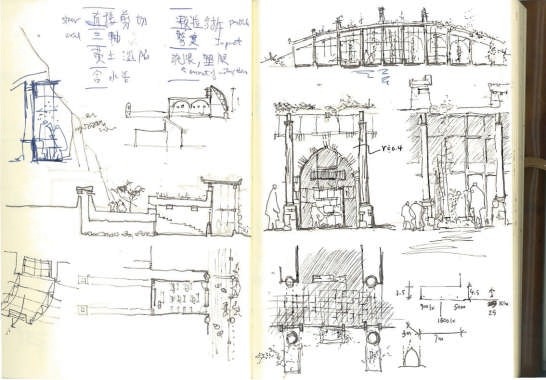
The project emphasizes a scientific and transferable methodology: condition analyses, computer simulation experiments and field construction. Condition analyses in economy & resource for building, climate, and vernacular architecture deduce that thermal design for this region is the most effective approach towards ecological architecture, and both design and construction should follow these principles: comfortable indoor ambience, cost-effectiveness, minimum embodied energy and construction ease. The investigation is further by with thermal simulation experiments. By filtering and optimizing locally available materials and techniques, it is found that the most basic techniques of thermal mass and insulation based on earth and natural materials and be very effective; they should be strategically employed.
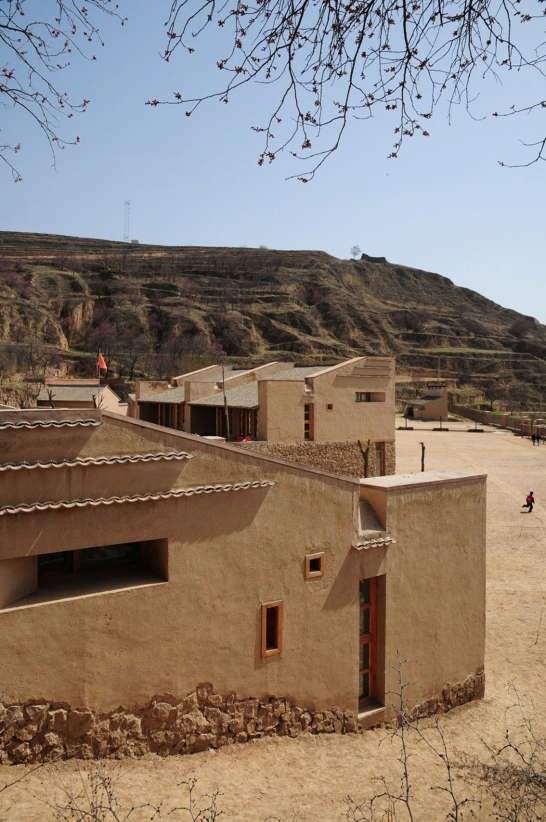
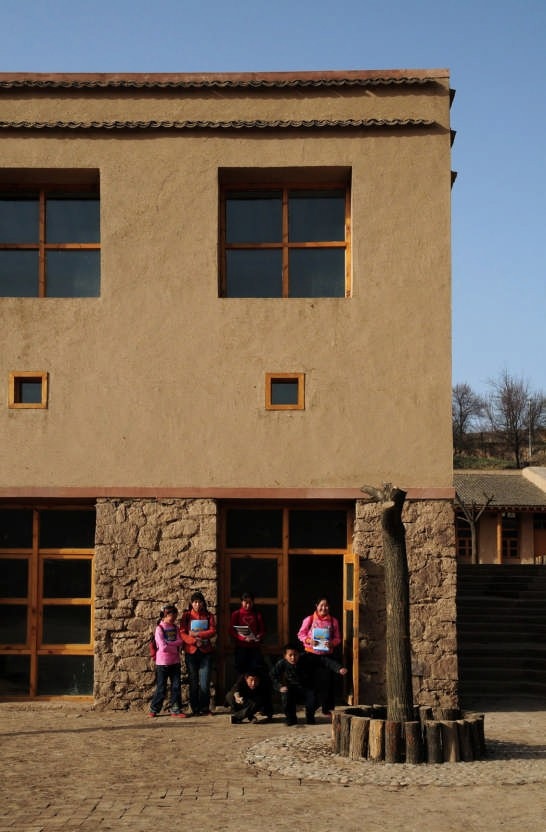
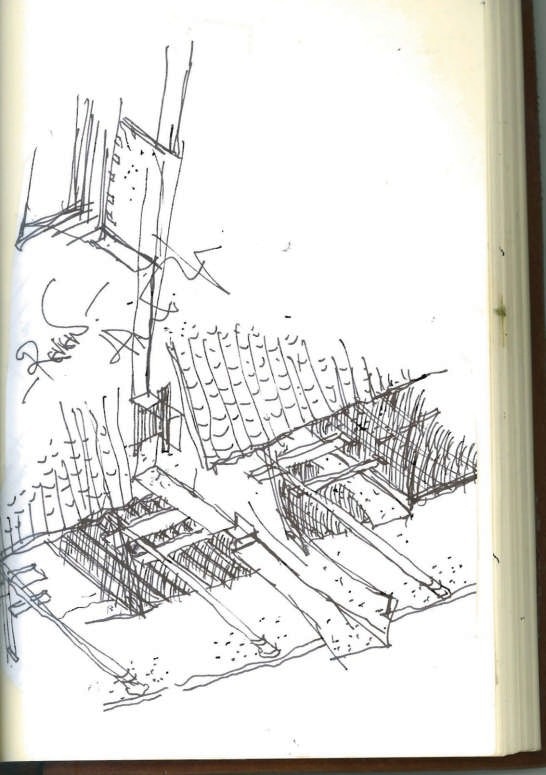
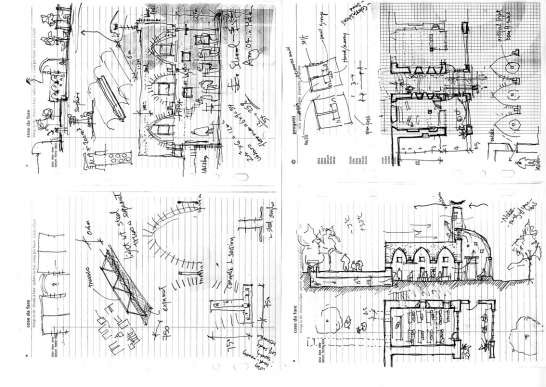
Follow the topography, 10 proposed classrooms are planned into 5 units at two levels for maximum exposure to daylight and natural ventilation in summer. A tree-based landscape helps to create a desirable campus ambience for children. The classroom form is derived from local traditional houses with timber structures so as to be constructed easily by villagers. Thermal mass and insulation are employed in the forms of mud-brick walls, the insulated traditional roof, double-glazed windows, etc. The semi-buried form at the north side together with the direct-gain mode of passive solar system can further upgrade the thermal performance. Daylight to the indoor space is maximised by the angled opening of windows.
Materials and Construction
“Instead of buying and using cheaper factory made red tiles, we told the village head to go around to the homes of villagers to collect and buy un-used roof tiles to be recycled.”
The construction inherited the local traditional means. It was implemented by the villagers themselves mostly with simple traditional tools. Most building materials, such as mud bricks, rubble, straw and reed, are sourced in or around the site with minimum embodied energy. Also due to the involvement of these natural materials, little waste was generated during construction, off-cut were recycled back into construction, for example off-cut rafter reused for children’s facilities, spare mud bricks mixed with straw mud for plaster. The construction has almost no environmental impact.
Measurement and Evaluation
The construction of the new school was completed in summer 2007. The direct construction cost for materials, equipments and manpower is around HKD$422/mq, far cheaper than local conventional classrooms made of bricks and concrete. The new school has been used by children and teachers since September, 2007. According to field measurements last year, the indoor air temperature of new classrooms is always stable, cool in summer and warm in winter. Even in the last winter’s infrequent cold temperatures, the indoor ambience could still reach an acceptable thermal comfort with fresh air, without needing coal for heating.
Deliverables
In conclusion, the followings are achieved: firstly, the new school creates a comfortable and desirable campus ambience for the children. Furthermore, compared to local conventional schools, during its whole life cycle it contributes a far better ecological performance in indoor comfort, energy consumption and environmental impact.
Secondly, as a charity project, most of the donation was shared within the village community due to employing the local villagers and using their resources.
The last and most important point, with the eco-school project the villagers can re-understand their own tradition. The school illustrates to the locals a feasible way towards an ecological architecture suited for the conditions of China’s Loess Plateau region. In this way, by selectively employing their familiar techniques and materials the villagers can easily build themselves their most effective and affordable ecological buildings.
Postscript
Last but not least, quoting the school master, “From now on, not one piece of coal needs to be burned to keep warm. All our money can be spent on books.”
Edward Ng and Jun Mu